Do you wonder how sunlight is converted into electricity? No magic, no miracle, it’s pure science. And the element responsible for this transformation is a tiny object —the photovoltaic cell, or PV cell.
Are you planning to set up a solar cell power plant? Or are you curious to understand what a solar cell is, how it works, and about its cost?
You have arrived at the right place. This article straightforwardly explores these details.
What Is a Solar Cell (Photovoltaic Cell)?
A solar cell is a tiny device that resides in the solar panel. It is responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. You can say it’s one of the vital components of solar panels.
A solar cell converts sunlight directly into electricity. As the basic unit of solar panels, it forms the very foundation of solar energy systems.
Sunlight activates the cell, sending electrons through a circuit and generating electricity—just that simple.
How Does Solar Light Become Electricity?
Let’s understand how solar photovoltaic cells work:
- Light Absorption: Sunlight hits the solar cell.
- Charge Carrier Separation: The sunlight energy releases electrons. These electrons leave holes behind.
- Extraction: Electrons move through the p-n junction. This movement generates an electric current.
This process is the photovoltaic effect. This effect powers everything from satellites to streetlights.
What Are Solar Cells Made Up Of?
Solar cells may look thin and flat, but they’re built from materials that do powerful work. Let’s first understand what they’re made of.
Each layer plays a key role in turning sunlight into usable electricity.
Let’s break it down:
| Component | Role in Solar Cell |
| Silicon Semiconductors | Main material for converting sunlight |
| P-N Junction | Separates charges to create a current |
| Doping Elements | Boron (p-type), Phosphorus (n-type) |
| Glass | Acts as a protective cover for the cell from the weather |
| Plastic | Adds flexibility and insulation |
| Aluminium & Copper | Conducts electricity and supports the structure |
This proves photovoltaic cells are made up of more than just silicon; they’re a smart mix of science and engineering.
Working Principle of Solar PV Cells
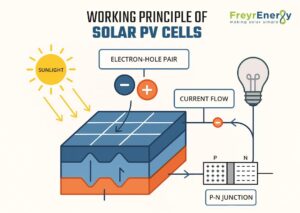
Solar PV cells might look simple, but there’s smart science behind how they turn sunlight into electricity. To understand how they work, let’s break down the process into easy steps.
It all starts when sunlight hits the surface of the solar cell.
- Sunlight falls on the cell
- Electron-hole is created
- Current flow via p-n junction.
Solar Cells Types (PV Cells)
Over the years, you can notice a lot of improvements in solar technology. Let’s explore types of solar cells:
First-Generation: Silicon-Based
| Type | Description | Efficiency | Cost |
| Monocrystalline | Made from single-crystal silicon | High | Higher |
| Polycrystalline | Made from multiple crystals | Medium | Affordable |
These are the most common in rooftop and solar cell power plant setups.
Second-Generation: Thin-Film Solar Cells
| Type | Description | Efficiency | Flexibility |
| Amorphous Silicon | Thin and lightweight | Low | High |
| CdTe | Cadmium Telluride-based | Medium | Moderate |
| CIGS | Copper Indium Gallium Selenide | Medium | High |
Thin-film solar cells are great for portable and flexible applications.
Third-Generation: Emerging Technologies
Multijunction Solar Cells
These cell has multiple layers. It helps them to capture a broader range of sunlight. They are popular for their best efficiency. Satellites and concentrated photovoltaics (CPV) use multijunction solar cells.
Organic Solar Cells
Another name for these cells is organic photovoltaic cells or organic cells. They use organic semiconductors. Organic solar cells are lightweight, flexible, and even transparent. However, they have lower efficiency and shorter lifespans.
Perovskite Solar Cells
Perovskite cells are new to the club. Their manufacturing cost is low. Yet they offer high efficiency. The downside is that there are challenges such as stability and lead toxicity, which need to be addressed.
Solar Cell Efficiency and Cost
Solar cell efficiency depends on:
- Material quality
- Weather and temperature
- Irradiance (sunlight intensity)
There’s a theoretical limit called the Shockley–Queisser limit. It limits the amount of sunlight that can be converted. Therefore, manufacturers strike a balance between high-efficiency solar cells and affordability.
| Type of Cell | Efficiency Range | Solar Cell Price per Watt |
| Monocrystalline | 18–22% | ₹25 – ₹35 |
| Polycrystalline | 15–18% | ₹20 – ₹28 |
| Thin-Film | 10–12% | ₹18 – ₹25 |
| Perovskite (lab) | 25%+ | ₹15 – ₹20 (projected) |
Note: Prices vary by brand, location, and bulk purchase.
Applications of Solar Cells
Solar cells are no longer limited to rooftops or large fields. They’ve quietly become part of our everyday lives.
Let’s explore where these powerful little devices are being used today.
Solar Power Plants
Solar power plants are revolutionising the way we generate electricity on a large scale. They use sunlight to generate clean energy for entire cities and industries.
Let’s take a quick look at how these systems are shaping India’s energy future.
Solar Cell 12V Uses
Perfect for off-grid setups like:
- RVs and campers
- Marine applications
- Traffic signals
- Small electronics
- Backup power systems
Conclusion
Solar cells have come a long way over the years. Starting from basic silicon panels to advanced perovskite and multijunction designs. Homes, industries and even space missions use solar cells to power themselves.
Solar cell efficiency continues to improve day by day, accompanied by a decrease in solar cell prices. India’s clean energy journey is set to take off in a short period.
Now is the time to start planning for a solar cell power plant and explore more about solar PV cells.
Reach out to Freyr Energy for expert guidance, affordable solutions, and smooth installation. Let’s light up your future, one photon at a time.
