We can see that solar PV systems are increasingly being installed across the country as a means to address climate change. There are many types of solar systems, of which a grid-connected PV system is one.
This blog is all about grid-connected solar systems, their types, and benefits. Read further to learn more.
What is a grid-connected PV system?
A grid-connected solar system is a solar system that is connected to the power grid that supplies electricity. It is connected through a bi-directional net meter and is also called an on-grid or grid-tied PV system.
When your solar system is grid-connected, you can send the excess energy generated back to the grid and earn credits for the same.
Types of grid-connected PV systems
There are generally two types of grid-tied solar systems: on-grid and hybrid.
On-grid
It is the most popularly used system. Here, the solar system is connected to the common grid. After domestic consumption, when there is surplus electricity generated by the solar system, the same is directly taken back to the grid.
Hybrid PV system
This is an on-grid system along with a battery storage facility. Here, the excess energy is stored in batteries and can be used during times of outages. It is a combination of on-grid and off-grid systems.
Components in an on-grid solar system
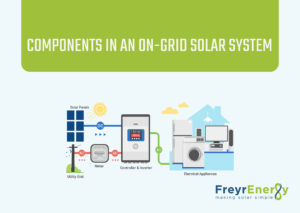
1. Solar panels
They are the main components in a grid-connected system. Solar panels contain multiple photovoltaic (PV) cells that capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. There are many different kinds of solar panels, such as monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin-film, concentrated, PERC, and bifacial panels.
2. Solar inverters
The electricity produced by solar panels is direct current(DC), which cannot be used to power appliances. It is converted into alternating current (AC) by inverters so that it can be used by connected devices and appliances.
3. Mounting structure
Strong solar mounting structures to support the solar panels are created. They bear the weight of the system and support it for seamless performance.
4. Bi-directional meters
A bidirectional meter can control the flow of current between the grid and the solar system. During periods of excess energy generation, these meters transfer energy to the grid. During winters when energy production is low, it is taken back from the grid to power homes.
With net metering, the power grid credits consumers for the energy they receive. This enables further reduction in electricity bills.
5. Grid
The grid is the common grid, which supplies electricity. The PV system is connected to the grid to enable the flow of energy.
Working of a grid-connected PV system
- The rooftop solar panels draw sunlight during the day and generate electricity.
- The electricity generated is converted into a usable form, which is alternating current, by the inverters.
- Now, all the connected appliances of your home are powered with the AC current.
- When there is any surplus energy left after domestic consumption, it is sent to the utility grid of the discoms.
- The bidirectional meter makes it easy to transfer excess electricity.
- The discoms credit you for the amount of electricity they receive.
- When there is insufficient power generation by solar panels due to weather conditions, the excess stored in batteries can be used or imported back from the grid.
Merits and demerits of an on-grid system
Merits
Lowers electricity bills
Consumers can experience a reduction in power bills as they also earn credits for excess energy transfer.
Reliable supply
Since the PV system is connected to the grid, it ensures a continuous supply.
Easy to install
Grid-tied PV systems are easy to install and do not require heavy upfront costs.
Scalable
On-grid systems can be scaled based on future increases in consumption.
Easy maintenance
Maintenance of a grid-connected PV system is easy with a professional solar company.
Demerits
Grid dependence
There is still grid dependence during low sunlight days and winters when production is less.
Additional cost
Some distribution companies charge additional fees for connection to the grid.
Cost of installing a grid-connected PV system
There are several factors affecting the cost of installation of a grid-connected PV system. This includes the size of the solar system, location, government subsidies, cost of components used, Discom charges, and more.
Typically, a 1kW system may cost between ₹45,000 and ₹ 60,000. As the system size increases, the cost also increases.
Conclusion
A grid-connected PV system has several advantages for the consumer and the environment. Along with ensuring a constant supply of electricity, it also allows households to sell excess power and earn from it.
Make sure to discuss the merits of the grid-tied solar system with your solar company before you commence installation of your rooftop solar panels.
